What Is Structured Data (AKA Schema or MicroData) and How Is Structured Data Used for SEO?
Sometimes, it is the small things that change the way search engines see and understand our websites. Structured Data has been used more over the years by search engines to help categorize and understand websites and their associated content. You may also hear structured data referred to as microdata or schema markup. When developers and SEO companies are using any of these terms, they are more than likely using them interchangeably, even though that may not be the “most” accurate.
For example, inline HTML microdata was only used to nest metadata within the HTML content itself and is no longer the preferred method of adding schema to a page. Now, structured data is implemented into a website’s code using JSON-LD as the preferred method.
The important element is not which terminology is most appropriate, but what overall impact utilizing this unique tool can have on your web presence. For the sake of this article, we will refer to all the various terminologies as simply “structured data” or “schema.”
Table of Contents
What Does Structured Data Do?
It is hard to immediately grasp how structured data works, especially if you are new to web development. You most likely have heard the term HTML, which, put simply, is what is responsible for showing the content (text and images) on your website. Think of structured data as extra “behind-the-scenes” code that is not visible but provides the context of your content.
For example, if you have a phone number listed on your website inside of the content, Google probably understands that the group of 10 characters is a phone number, but it doesn’t know if it’s your company’s phone number, or the customer support line of one of your vendors you are referencing within the page. Structured data allows you to draw connections between the content and how it relates to your visitor’s overall need for access to pertinent information.
A significant benefit of using structured data is that it helps provide search engines with more context. In turn, context helps search engines better understand, index, and, indirectly, rank your website. This type of schema markup is also responsible for improving eligibility for "rich snippets" (AKA rich results) that display additional formatted information within the search results. You’ve likely seen rich snippets within Google Search which can show in the form of details about a business, listicles, answer to a FAQ, product carousels, reviews, events, etc.
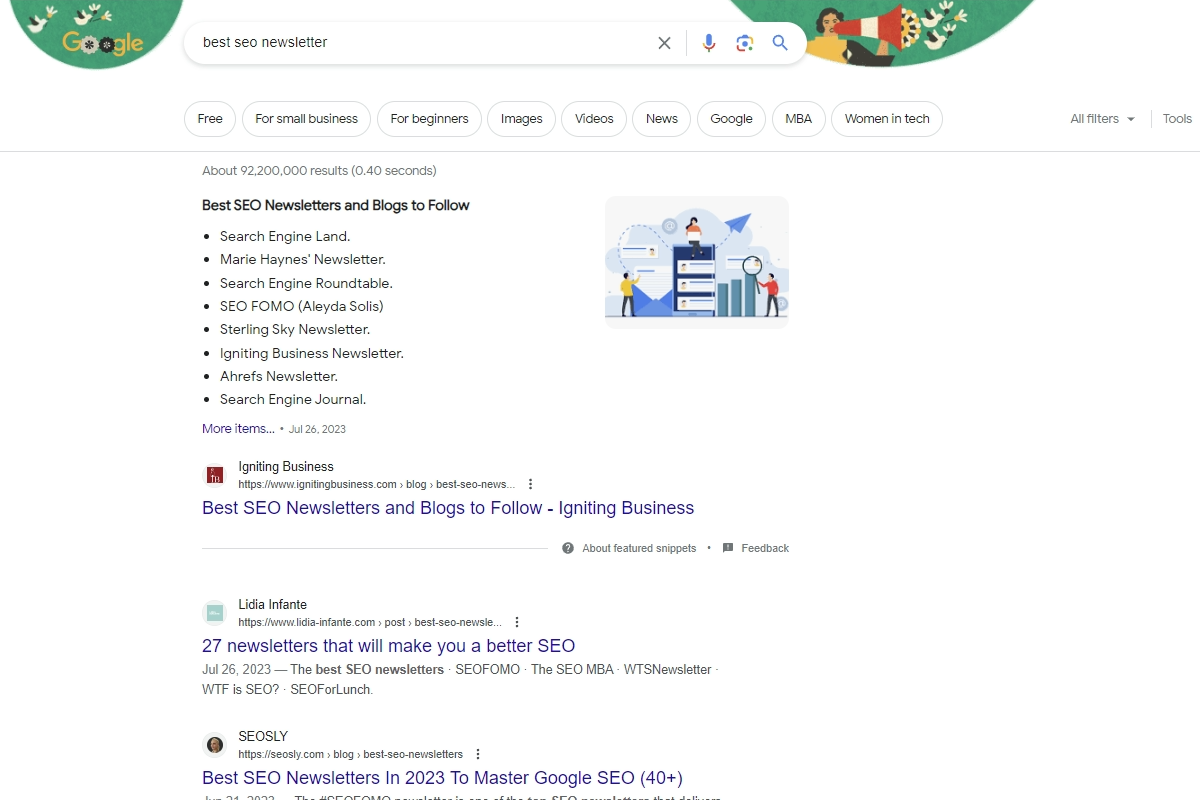
For example, take a look at the image capture below that shows a rich snippet for the search phrase “best seo newsletter” This result appears above the rest of the search results, in what we affectionately call position 0, with a preview of the text and attribution to the publishing author.
Search engines love to display rich snippets when it can enhance the searcher’s experience with relevant and accurate data. To do so, they must have data to pull from which incorporates more content than simply the page title and meta description.
While Google is getting better and better at understanding the content, even without structured data, implementing schema properly can still help to make the search engine’s job a little bit easier.
Using Schema
There are numerous different types of structured data and schemas that can be included on your website. Keep in mind that arbitrarily stuffing irrelevant schema markup into your page will not improve your Google rankings.
Structured data should and must relate to the main topic of your page and correspond with content that is already visible on the page. While search engines look at many different factors when it comes to ranking a website, adding the correct schema can help. Google, Bing, and Yahoo all use structured data to varying degrees.
Google Supported Vs. Unsupported Structured Data Markup
Google has a limited number of officially “supported” structured data types. Technically, these supported types are what can help your website be eligible for a rich result within a Google search engine result page (SERP).
However, it’s critical to keep in mind that there are hundreds of types of schemas listed on schema.org which is a project co-sponsored by Google, Microsoft, Yahoo, and Yandex to encourage the adoption of utilizing structured data in hopes of improving search and overall user experience. In other words, even if Google doesn’t “officially” support a specific schema yet, that doesn’t mean it’s not used to help search engines understand the content on your page. Additionally, Google updates their officially supported frequently, so why not get a head start?
Common Types of Structured Data
Many modern Content Management Systems (CMS) incorporate very basic schema into your website like the “Article” schema or “Breadcrumbs” schema. However, more advanced and helpful schemas typically need to be configured separately.
Some commonly used structured data types include the following:
- Article
- Person
- Book
- Breadcrumb
- Course
- Event
- Fact Check
- FAQ
- Job Posting
- Local Business
- Logo
- Movie
- Product
- Q&A
- Recipe
- Review
- Software App
- Video
You can view the full of schemas available at schema.org.
Test and Improve Your Website’s Schema and Rich Result Eligibility
We encourage you to explore different schemas and see how they can complement the content of your website. Additionally, if you’re not sure what schema is already present on your site, and whether it’s showing the correct information, here are a few tools to help you get started:
- Google’s Rich Results Test – This tool is used to check the validity of any schemas that are officially supported by Google (remember, that this is a smaller subset of structured data).
- Schema Markup Validator – For many years, this tool was hosted directly by Google. However, it eventually was moved to schema.org. Unlike the Rich Results Test, the Schema Markup Validator tests against a much larger set of schemas available on schema.org.
- Semrush – This is a commercial SEO software platform that will not only test what schema you have present, but also give you hundreds of other insights regarding SEO issues that can and should be addressed. You can get a free trial of Semrush and run a site audit to see what schemas are in place. From our experience, Semrush is hands down one of the best SEO toolsets out there.
For access to more SEO and web design tips, consider signing up for our free monthly newsletter.
At no additional cost to you, we may receive a commission if you click on some of the links on this website and make a purchase.
About the author
Ben Seidel is the CEO and Founder of Igniting Business. Ben has been serving hundreds of small businesses with web design and SEO services for over 15 years and covering digital marketing related topics since 2012.
Over the years, Ben has been recognized on a local and national level, including entrepreneurship awards from both the NFIB and NASE and being featured in publications such as CNBC Universal, Yahoo News, Intuit Small Business, CIO.com, Mizzou Magazine, and Fox Business.